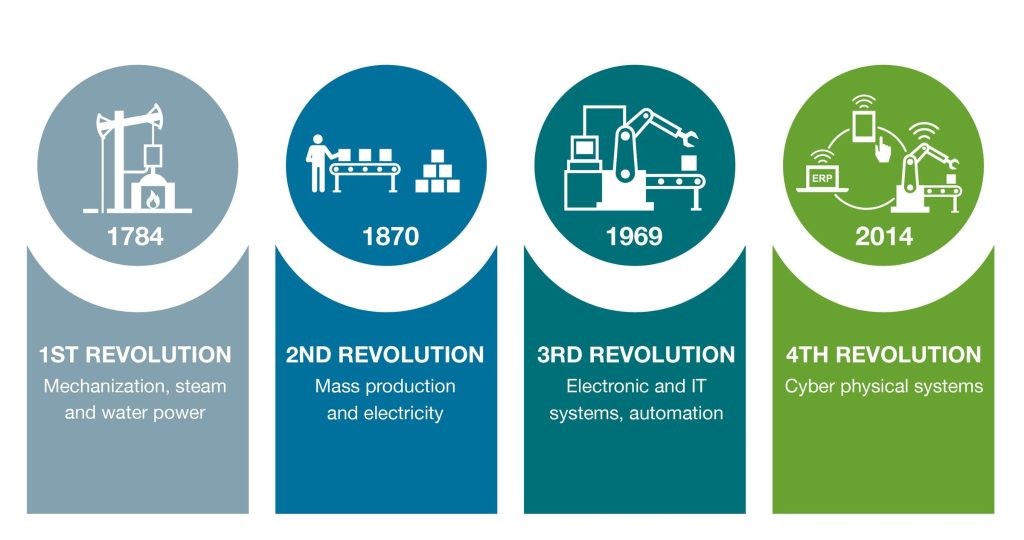
The Industry 4.0 Revolution is transforming every sector of the global economy, from manufacturing and transportation to education and healthcare. This revolution is driven by the integration of technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), blockchain, and automation, leading to unprecedented advancements that improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. In this article, we will explore the components of the Industry 4.0 Revolution, its impact on society, and the opportunities and challenges it presents.

1. What is the Industry 4.0 Revolution?
- The Industry 4.0 Revolution refers to the shift from traditional manufacturing methods to the use of cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data. This revolution not only affects the production process but also changes how people work and live. It is characterized by the integration of physical systems with digital technologies, enabling industries to become more automated, data-driven, and interconnected.
- One key feature of Industry 4.0 is the use of smart devices and sensors that communicate with each other in real-time, providing manufacturers with critical data on production processes. This allows for predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and optimizing manufacturing efficiency. For example, companies can now monitor machine performance and detect potential failures before they occur, thereby reducing maintenance costs and increasing productivity.
2. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Industry 4.0
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the driving forces behind the Industry 4.0 Revolution. AI systems enable machines to learn from data and perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence, such as decision-making, problem-solving, and pattern recognition. This technology is being used across various industries to improve operations and make processes more efficient.
- In manufacturing, AI is being applied to optimize supply chains, improve quality control, and automate routine tasks. For instance, AI-powered robots can be used to perform repetitive assembly tasks, reducing human error and increasing production speed. Additionally, AI is helping businesses analyze big data to forecast demand and optimize inventory, ensuring that manufacturers can meet customer needs in a timely manner.
- AI is also playing a significant role in the development of autonomous systems. In the automotive industry, for example, AI is enabling the creation of self-driving cars, which rely on machine learning algorithms to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make real-time decisions without human intervention.
3. The Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Manufacturing
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is another critical component of the Industry 4.0 Revolution. IoT refers to the network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that allow them to collect and exchange data. In smart manufacturing, IoT devices are used to monitor and control industrial equipment remotely, providing real-time insights into production processes.
- With IoT, manufacturers can optimize production lines, monitor energy consumption, and improve product quality by tracking every aspect of the manufacturing process. For example, sensors installed in machines can detect vibrations, temperature changes, and other indicators that signal when maintenance is needed. This capability allows for predictive maintenance, where potential issues are addressed before they cause downtime, ultimately increasing efficiency and reducing operating costs.
4. Blockchain Technology and Its Impact on Industry 4.0
- Blockchain technology, best known for its use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is also playing a vital role in the Industry 4.0 Revolution. Blockchain provides a secure, transparent, and decentralized way to record transactions, which is crucial for industries that rely on data integrity and security.
- In the manufacturing sector, blockchain is being used to improve supply chain transparency by tracking the movement of goods in real-time. This technology ensures that all transactions are recorded and verified, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. By implementing blockchain, businesses can ensure that products are sourced responsibly and meet quality standards, which is especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals and food.
- Moreover, blockchain technology can be used to streamline operations and automate contract management through smart contracts. These contracts are self-executing agreements where the terms are written into code, allowing for automatic execution when predefined conditions are met. This reduces the need for intermediaries and simplifies the contract process.
5. The Future of Work in the Industry 4.0 Era
- The Industry 4.0 Revolution is reshaping the workforce by introducing automation and AI into the workplace. While automation and robotics improve efficiency and reduce costs, they also raise concerns about job displacement. Many routine and manual tasks are being taken over by machines, leading to the need for workers to develop new skills.
- To adapt to these changes, there will be a growing demand for workers with expertise in digital technologies, data analysis, and AI. Industries will need workers who can design, maintain, and manage AI systems, as well as those who can interpret data to drive business decisions. Reskilling and upskilling will be essential to ensure that workers are prepared for the evolving job market.
- Furthermore, the Industry 4.0 Revolution is giving rise to new job roles that didn’t exist before. For example, data scientists, AI specialists, and IoT engineers are becoming crucial members of the workforce. These positions will continue to grow as industries increasingly rely on digital technologies to stay competitive.
6. Opportunities and Challenges of Industry 4.0
- The Industry 4.0 Revolution offers numerous opportunities for businesses and industries. Companies can benefit from increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved product quality. The adoption of smart technologies allows businesses to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market and respond quickly to customer demands.
- However, there are also significant challenges. One of the main concerns is the security and privacy of data. As more devices and systems become connected, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Companies will need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of their systems.
- Another challenge is the need for continuous innovation. The pace of technological advancement is accelerating, and businesses must stay ahead of the curve to maintain their competitive edge. This requires investment in research and development and a culture of innovation within the company.
7. Conclusion: The Future of Industry 4.0
- The Industry 4.0 Revolution is already having a profound impact on industries and societies around the world. As technologies like AI, IoT, blockchain, and automation continue to evolve, they will continue to drive innovation and change in ways we can’t yet fully imagine. While the Industry 4.0 Revolution brings new opportunities, it also presents challenges that must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition to the future of work and production.
- As we move forward, it is crucial for businesses, workers, and governments to work together to leverage these technologies responsibly, ensuring that the benefits of the Industry 4.0 Revolution are shared by all and that no one is left behind.
In conclusion, the Industry 4.0 Revolution is more than just a trend; it is the foundation for the future of work, manufacturing, and many other sectors. Embracing it with the right strategies, training, and technologies will unlock new levels of potential for industries and individuals alike, creating a future that is smarter, more connected, and more efficient than ever before.